实验室3篇论文被国际人工智能联合会议IJCAI-ECAI 2022接收.
IRIP实验室今年共有3篇论文被国际人工智能联合会议IJCAI-ECAI 2022接收!IJCAI 是人工智能领域中最主要的学术会议之一,原为单数年召开,自2015年起改为每年召开,本次IJCAI与ECAI一起召开。IJCAI官网显示,此次会议有4535篇的大会论文投稿,录取率仅为15%。此次会议将于2022年7月在维也纳召开。
接收论文简要介绍如下:
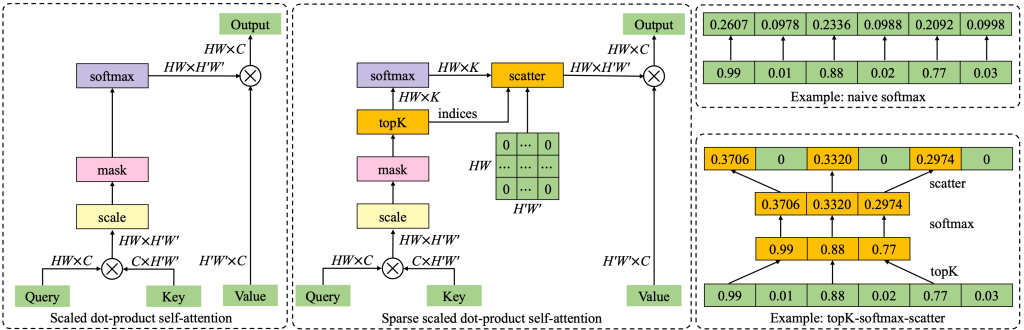
1. SparseTT: Visual Tracking with Sparse Transformers. (Zhihong Fu, Zehua Fu, Qingjie Liu, Wenrui Cai, Yunhong Wang) (long oral presentation)
近年来,Transformer被成功地应用到目标跟踪领域并显著提升了跟踪器的性能。其中的关键因素是自注意力机制。然而,由于自注意力机制缺乏对搜索区域主要信息的重点关注,因此该机制容易导致跟踪过程受无关背景信息干扰。针对该问题,本文利用稀疏注意力机制促使跟踪器聚焦搜索区域的最相关信息,极大地提高了跟踪的准确性。此外,本文向目标跟踪领域引入了一种有利于提升前背景分类和目标边界框回归准确性的通用的双头预测器,进一步提高了跟踪的性能。大量的实验验证了本文提出方法的优越性和实时性。值得一提的是,相比于最近目标跟踪领域十分流行的基于Transformer的高性能跟踪方法TransT,本文所提出方法的训练时间减少了75%,且性能更优,有利于促进目标跟踪领域的加速发展。
Transformers have been successfully applied to the visual tracking task and significantly promote tracking performance. The self-attention mechanism designed to model long-range dependencies is the key to the success of Transformers. However, self-attention lacks focusing on the most relevant information in the search regions, making it easy to be distracted by background. This paper relieves this issue with a sparse attention mechanism by focusing the most relevant information in the search regions, which enables a much accurate tracking. Furthermore, this paper introduces a double-head predictor to boost the accuracy of foreground-background classification and regression of target bounding boxes, which further improve the tracking performance. Extensive experiments show that, without bells and whistles, our method significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches on LaSOT, GOT-10k, TrackingNet, and UAV123, while running at 40 FPS. Notably, the training time of our method is reduced by 75% compared to that of TransT.
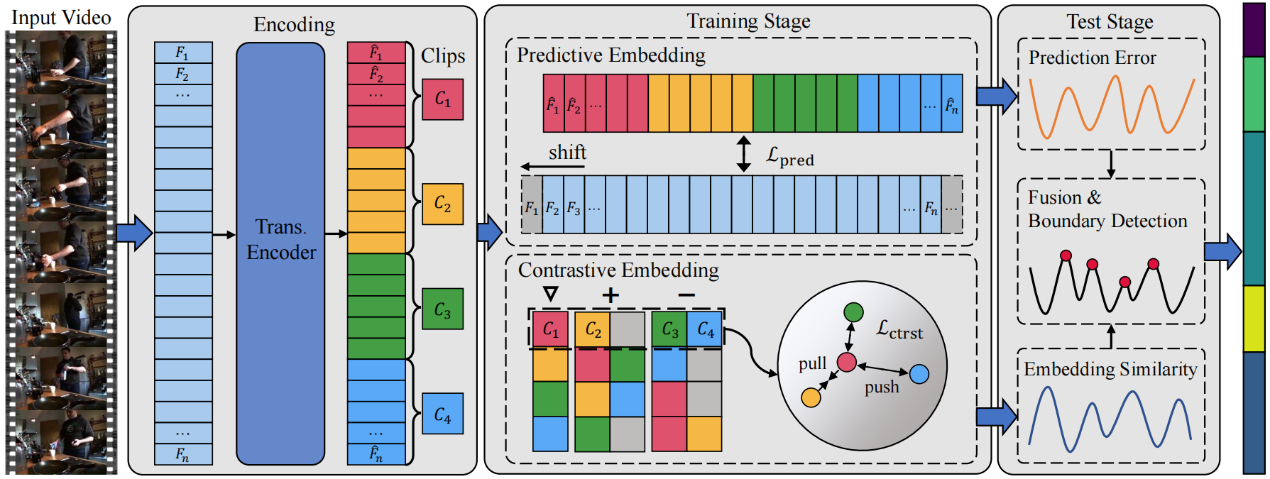
2. PACE: Predictive and Contrastive Embedding for Unsupervised Action Segmentation. (Jiahao Wang, Jie Qin, Yunhong Wang, Annan Li)
为了缓解视频动作分割领域密集时域标注成本高昂的问题,本文提出了一种适用于无监督场景的动作分割模型。由于现有基于预测或聚类的无监督动作分割方法容易出现过拟合及过分割的问题,我们提出一种基于预测与对比编码(PACE)的框架同时挖掘视频中的可预测性与相似度信息。在一个自回归Transformer编码器的基础上,我们利用帧级别预测编码获取视频内容的可预测信息,之后利用片段级别的对比编码挖掘动作语义的相似度信息,最后融合二者完成动作边界预测。通过在三个常用无监督动作分割数据库上进行详尽的实验,我们证明了所提出方法在性能上的显著优势。
Action segmentation, inferring temporal positions of human actions in an untrimmed video, is an important prerequisite for various video understanding tasks. Recently, unsupervised action segmentation (UAS) has emerged as a more challenging task due to the unavailability of frame-level annotations. Existing clustering- or prediction-based UAS approaches suffer from either over-segmentation or overfitting, leading to unsatisfactory results. To address those problems, we propose Predictive And Contrastive Embedding (PACE), a unified UAS framework leveraging both predictability and similarity information for more accurate action segmentation. On the basis of an auto-regressive transformer encoder, predictive embeddings are learned by exploiting the predictability of video context, while contrastive embeddings are generated by leveraging the similarity of adjacent short video clips. Extensive experiments on three challenging benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of our method, with up to 26.9% improvements in F1-score over the state of the art.
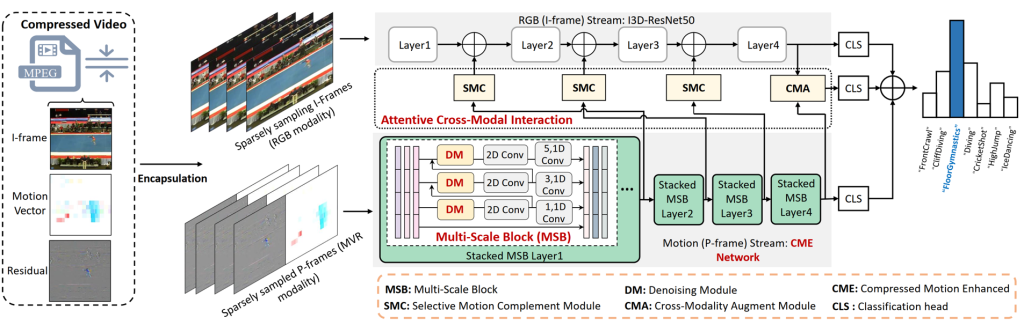
3.Representation Learning for Compressed Video Action Recognition via Attentive Cross-modal Interaction with Motion Enhancement. (Bing Li, Jiaxin Chen, Dongming Zhang, Xiuguo Bao, Di Huang)
针对压缩视频下的动作识别任务,本文提出了一种基于多尺度下运动信息增强、去噪和多模态交互的特征表示学习方法。通过多尺度的块设计引入更丰富的运动细节,而设计的去噪模块能够嵌入到多尺度模块下对粗糙的压缩运动模态进行去噪,从而达到增强压缩运动模态的目标。最后通过全局的多模态注意力模块和局部的时空注意力模块对不同层次下的压缩视频中的静态特征(I帧)和动态信息(运动向量和残差)进行交互融合,调整不同模态对不同动作识别下的重要性,从而提升模型的最终表现,而在Kinetics400、HMDB-51和UCF-101数据集上的实验证明了其优越性和有效性。
This paper proposes a feature representation learning method based on motion cues enhancement, denoising and multi-modality interaction at multiple scales for compressed video action recognition. Richer motion details are introduced through multi-scale block design, while the designed denoising module can be embedded to denoise coarse compressed motion modalities within multi-scale blocks, thus achieving the goal of enhancing compressed motion modalities. Finally, the static features (I-frames) and dynamic features (motion vectors and residuals) in compressed videos under different levels are interactively fused by the global multi-modallity attention module and the local spatio-temporal attention module to adjust the importance between different modalities under different actions, so as to enhance the final performance of the model. Experiments on the Kinetics400, HMDB-51 and UCF-101 datasetdemonstrate its superiority and effectiveness.