实验室4篇论文被国际计算机视觉与模式识别会议CVPR2023接收
IRIP实验室今年共有4篇论文被国际计算机视觉与模式识别会议CVPR 2023接收!CVPR是由IEEE主办的计算机视觉、模式识别及人工智能等领域最具影响力和最重要的国际顶级会议。CVPR官网显示,此次会议有9155篇的大会论文投稿,共录取2360篇论文,录取率约为25.78%。此次会议将于加拿大召开。
接收论文简要介绍如下:
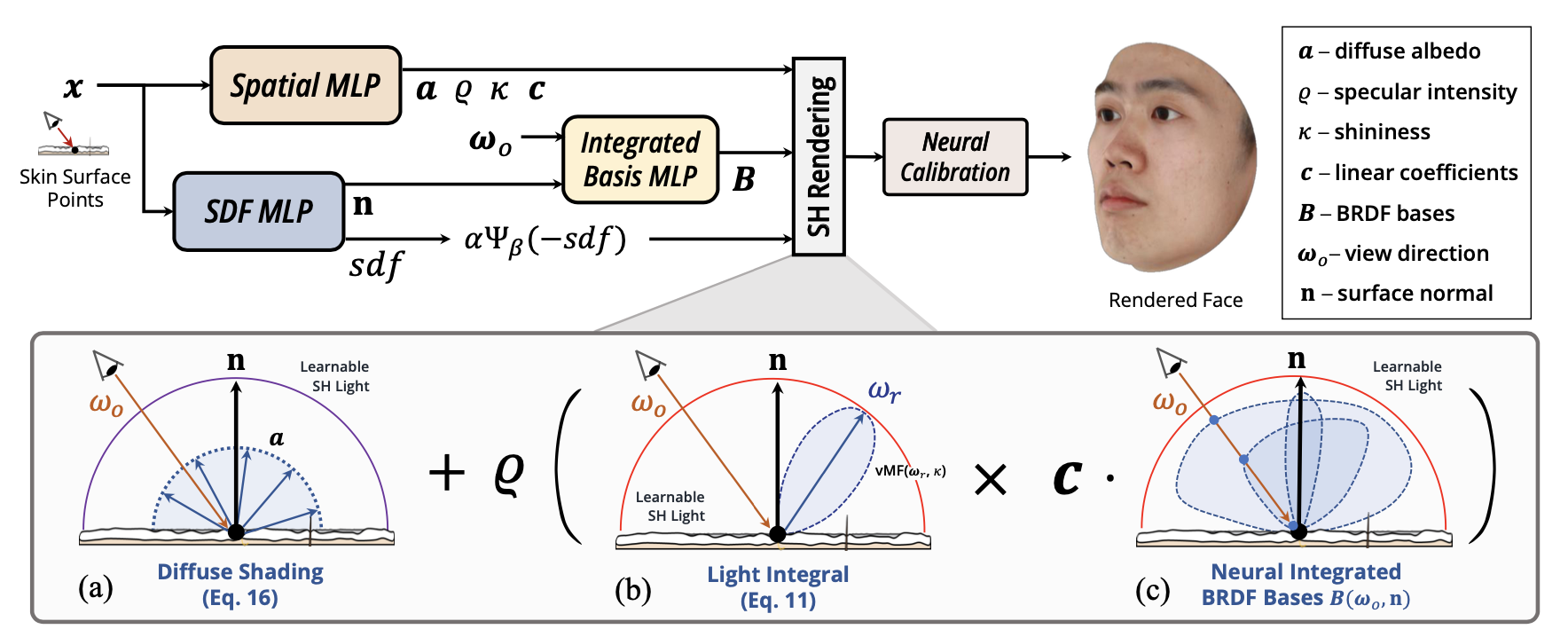
1.NeuFace: Realistic 3D Neural Face Rendering from Multi-view Images. (Mingwu Zheng, Haiyu Zhang, Hongyu Yang, Di Huang)
渲染多视角可重光照的真实感人脸是计算机视觉和计算机图形学在人脸相关应用上的核心内容。为了解决传统方法需要复杂的光照设置以及大量人力,神经渲染方法使用的物理先验不适用于人脸的问题,我们提出了一个基于物理和神经BRDF表示的渲染框架,通过使用人脸的低秩先验以及可微分的形状先验,可以从多视角数据重建高质量形状、表观属性的三维人脸模型。实验证明我们的模型在人脸重建上取得了优秀的结果,并且可以泛化到通用物体重建任务中。
Rendering realistic human faces with controllable view-points and lighting are beneficial to various computer vision and graphics applications. Due to complex lighting settings, manual efforts and physical prior used by neural rendering, which is not suitable for modeling the optical properties of multilayered facial skin. We propose a novel framework with naturally-bonded PBR and neural BRDF representations, namely NeuFace. We design a new low-rank prior and a differentiable SDF shape prior, i.e., ImFace, which significantly facilitate the learning of neural BRDFs and geometry field. Extensive experiments are performed to demonstrate the superiority of NeuFace, along with a decent generalization ability to common objects.
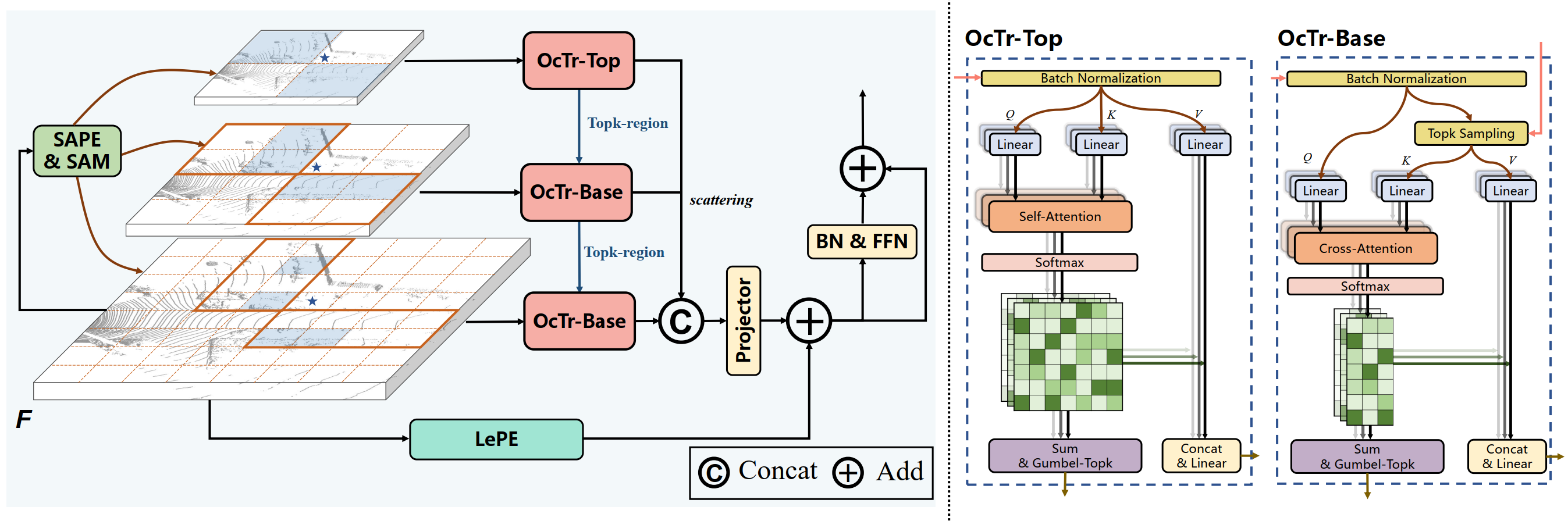
2.OcTr: Octree-based Transformer for 3D Object Detection. (Chao Zhou, Yanan Zhang, Jiaxin Chen, Di Huang)
当前基于Transformer的3D检测方法受限于不充足的感受野或粗粒度的整体相关性,不能很好地平衡准确性和效率。本文提出一种基于八叉树的Transformer主干网络OcTr来解决这个问题。该算法通过在顶层执行自注意力,然后递归地传播到受卦限约束的下层,在层次特征金字塔上构造一个动态八叉树,在控制计算复杂度的同时,由粗到精地捕获丰富的全局上下文。此外,为了增强前景感知,本文提出一种由语义感知位置嵌入和注意力mask组成的混合位置嵌入,以充分利用语义和几何线索。在Waymo和KITTI数据集上进行了大量实验,验证了其有效性。
The current Transformer-based 3D detection methods fail to properly balance the accuracy and efficiency, suffering from inadequate receptive fields or coarse-grained holistic correlations. In this paper, we propose an Octree-based Transformer, named OcTr, to address this issue. It constructs a dynamic octree on the hierarchical feature pyramid through conducting self-attention on the top level and then recursively propagates to the level below restricted by the octants, which captures rich global context in a coarse-to-fine manner while maintaining the computational complexity under control. Furthermore, for enhanced foreground perception, we propose a hybrid positional embedding, composed of the semantic-aware positional embedding and attention mask, to fully exploit semantic and geometry clues. Extensive experiments are conducted on the Waymo and KITTI Dataset, highlighting the effectiveness.
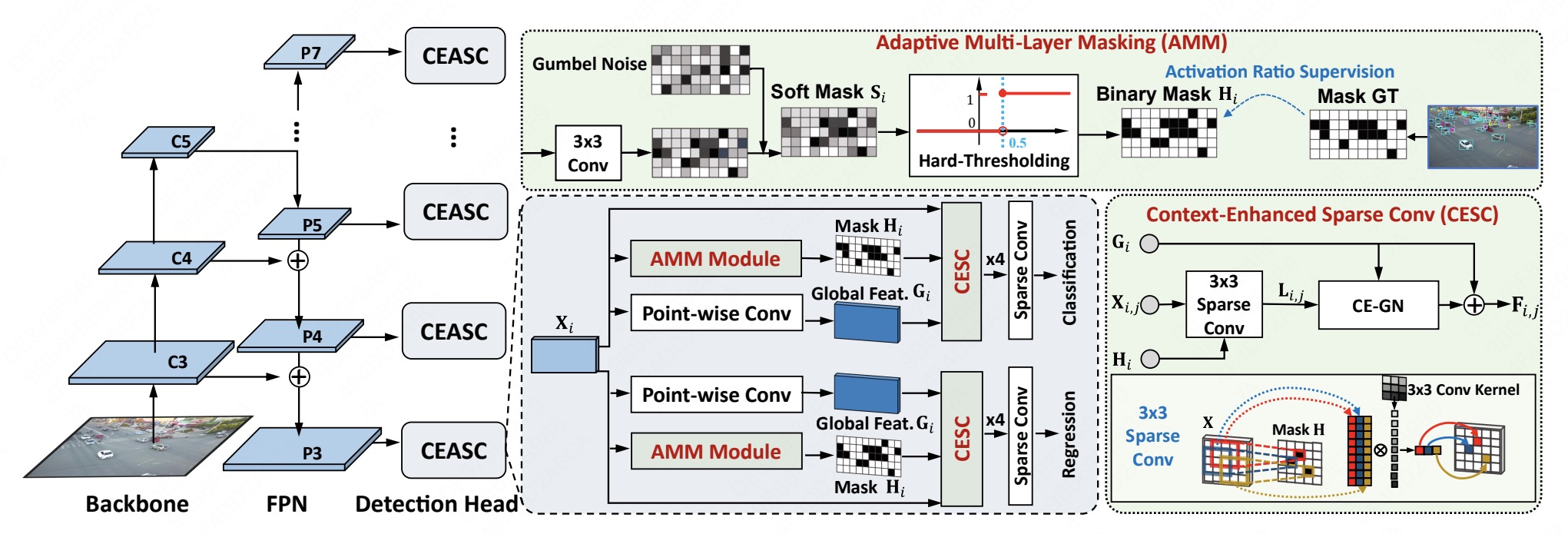
3.Adaptive Sparse Convolutional Networks with Global Context Enhancement for Faster Object Detection on Drone Images. (Bowei Du, Yecheng Huang, Jiaxin Chen, Di Huang)
本文提出了一种上下文增强的自适应稀疏卷积网络用于航拍图像的轻量化目标检测,旨在解决稀疏卷积存在的上下文信息缺失与不同前景区域尺度下的自适应稀疏掩码生成问题。模型设计了一个以上下文增强的组归一化层(CE-GN)为核心的上下文增强模块,将稀疏特征的分布特征替换为全局上下文分布维持分布结构并进一步融合上下文信息。同时设计了一种自适应掩码生成策略实现不同尺度下最优掩码比例的生成,提高模型加速效率。实验验证了我们方法的优越性。
The paper proposes an adaptive context-enhanced sparse convolutional network for lightweight object detection in aerial images, which aims to solve the problem of context information omission and realize adaptive sparse mask generation at different foreground area scales. A context-enhancement module based on context-enhanced GroupNorm (CE-GN) layer is designed. The distribution of sparse features is replaced by global context distribution to maintain feature structure and the module further integrates context information. At the same time, an adaptive mask generation strategy is designed to generate the optimal mask ratio at different scales and improve the model acceleration efficiency. Experiments prove the effectiveness of our method.
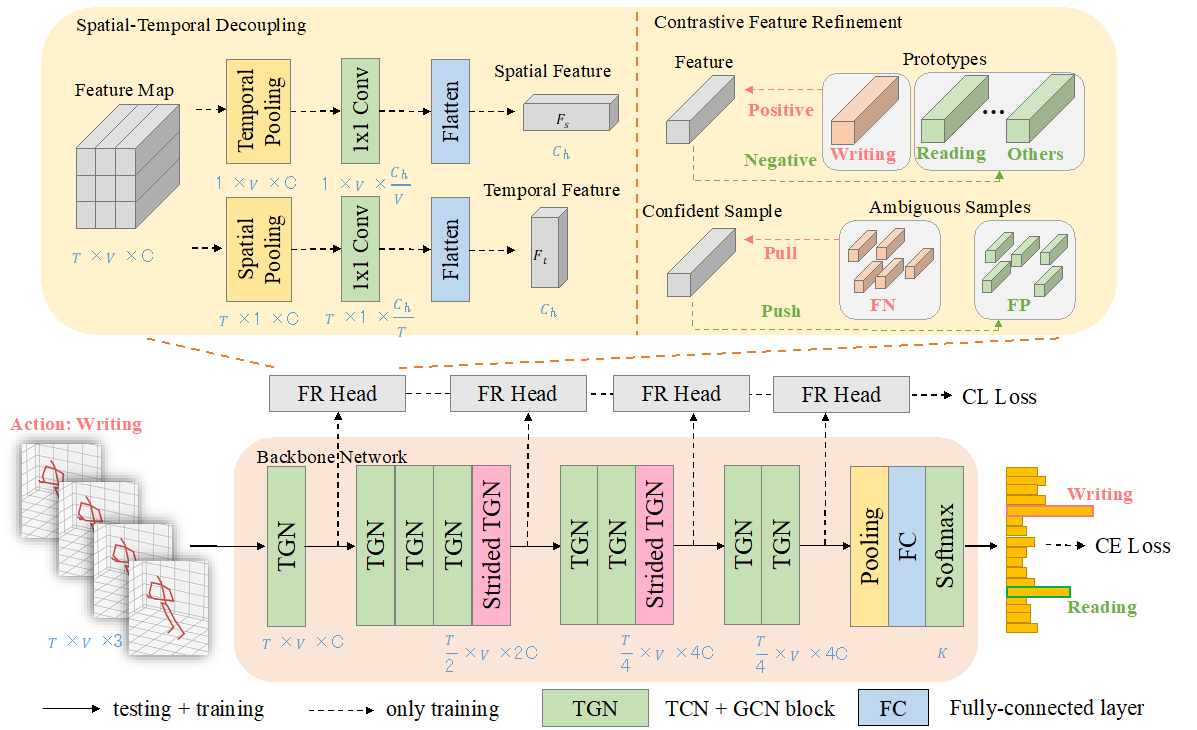
4.Learning Discriminative Representations for Skeleton Based Action Recognition. (Huanyu Zhou, Qingjie Liu, Yunhong Wang)
为了解决人体骨架动作分类任务中易混淆动作问题,本文提出了一种辅助的特征优化模块,通过对骨架特征的时空解耦以及基于对比学习的特征优化机制,学习具有判别性的人体骨架表征。本文在NTU RGB+D、NTU RGB+D 120和NW-UCLA三个常用人体骨架数据集上验证了其对易混淆动作的鉴别能力以及相对其他前沿模型的竞争力。
To solve the problem of ambiguous actions in skeleton based action recognition, this paper propose an auxiliary feature refinement head (FR Head), which consists of spatial-temporal decoupling and contrastive feature refinement, to obtain discriminative representations of skeletons. Extensive experiments are conducted on NTU RGB+D, NTU RGB+D 120, and NW-UCLA datasets. Our proposed models obtain competitive results from state-of-the-art methods and can help to discriminate those ambiguous samples.